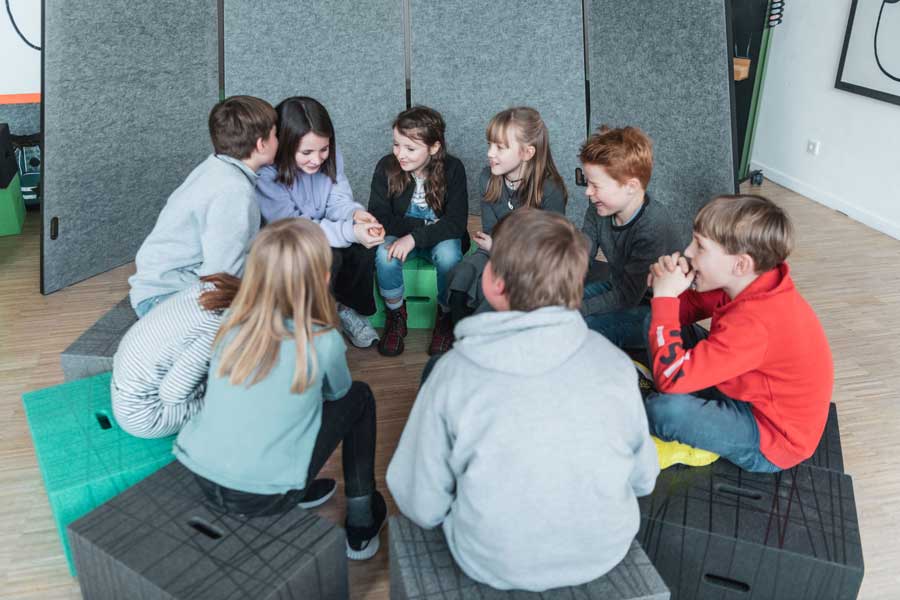

In today’s educational landscape, schools face numerous challenges that are inextricably linked to the profound changes in our society. Digitalization, individualization and new forms of work shape everyday school life and change the demands on our education system. Schools therefore not only see a duty to impart technical skills, but also to promote creative problem-solving skills, social skills and a high level of adaptability in students. At the same time, expectations are increasing to create a learning environment that addresses these diverse needs and not only supports children in learning, but also inspires them about what they have learned.
The modern learning landscape therefore requires innovative approaches that focus on flexibility and individuality. Static forms of teaching that were once common practice now quickly reach their limits. On the other hand, open learning concepts are becoming increasingly important because they better respond to the needs of individual students. They create space for creativity and personal responsibility and connect learning more closely with the requirements of the real world. But this realignment also brings with it concrete challenges:
Against this background, concepts such as the Chur model offer exciting solutions that rethink learning and view spatial design as the key to success. But what exactly is behind this approach and how does Xbrick come into play?
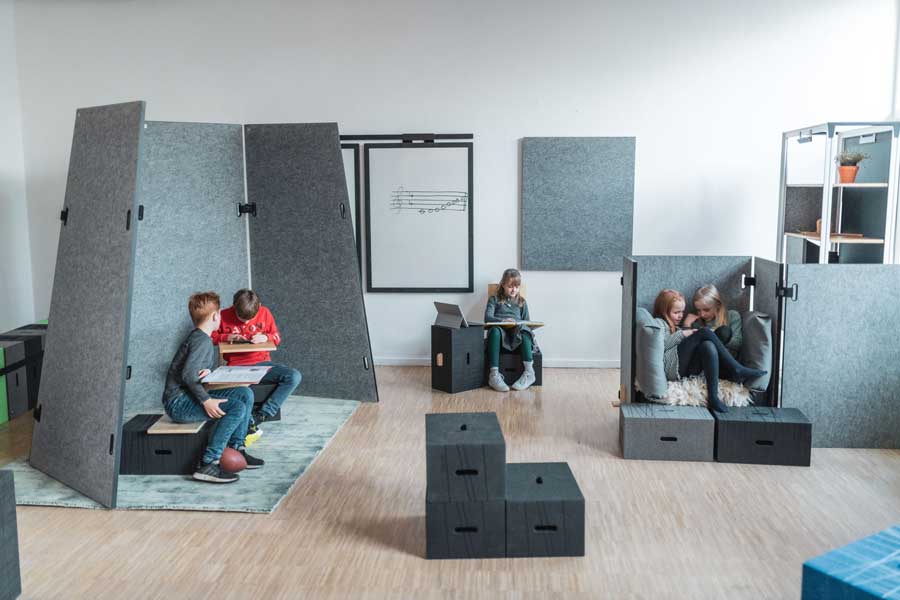

The Chur Model was developed in Switzerland in the 1990s, specifically in the canton of Graubünden, whose capital, Chur, gave the model its name. It originates from the work of Peter Fratton, a Swiss educator and reform pedagogue. Fratton was deeply engaged in exploring new learning methods and designed this concept to break away from traditional teaching approaches and create a flexible learning environment tailored to the individual needs of students.
The model was born out of the idea that learning is an individual and dynamic process, often hindered by rigid structures in everyday school life. The Chur Model utilizes self-organization and competency-based learning to create a learning landscape where students can learn independently and at their own pace. Lessons are no longer dominated by a fixed timetable or traditional classroom divisions but are replaced by dynamic structures adapted to students’ learning needs. The key characteristics include:
This model integrates various modern educational approaches and creates an environment that supports both individual development and collaborative learning.
It has probably already become clear at this point why Xbrick can play an important and supporting role in both lesson design and the overall school concept. Here are a brief summary of the advantages of Xbrick for everyday school life:
Xbrick supports new learning concepts by placing movement, flexibility and creative learning concepts in the foreground and making them easy to implement. Since you can start with just a few elements, this can easily be implemented as a retrofit in existing buildings with comparatively little investment. With its versatile application options, Xbrick not only supports the physical activity of students, but also creates an innovative environment that is tailored to the individual needs of modern learning methods.
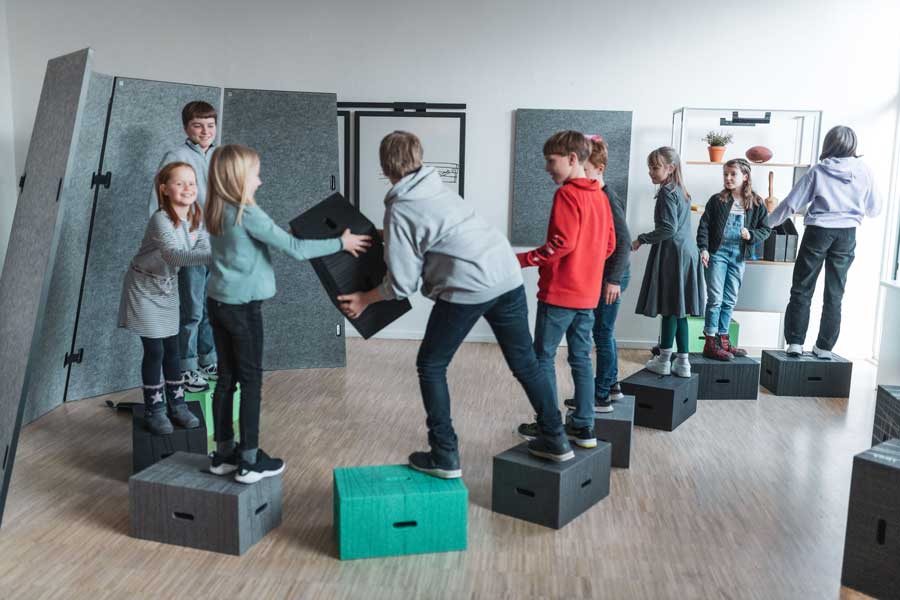

Xbrick promotes the intuitive integration of movement into lessons and offers students the opportunity to learn actively and creatively. The modules can be used in various contexts – whether as a seat, standing desk, pedestal or creative work surface. The students can create the optimal learning conditions for them depending on their needs and mood. Movement becomes an integral part of everyday school life and contributes to both concentration and well-being.
Modern learning concepts value individuality, which often means that students need their own rooms for focused work. With the portable Xbrick modules, such individual learning spaces can be set up quickly and easily – be it in the classroom, in the hallway or outdoors. This spatial flexibility makes it possible to effectively implement individualized learning processes and at the same time promotes the students’ personal responsibility.
Xbrick is characterized by its mobility and easy handling. The lightweight modules can be easily transported and rearranged by students of all ages. Whether as a single seat, in combination as a stand or even as a temporary work surface – Xbrick adapts to every teaching situation. This means that rooms can be redesigned again and again without much effort, creating a dynamic and inspiring learning atmosphere.
With Xbrick, lessons become flexible and location-independent. No matter whether in the schoolyard, in the park or in the hallway – the modules make it possible to move the learning space quickly and easily. This spatial variety not only offers new inspiration for teachers and students, but also contributes to the general well-being and motivation of the students.
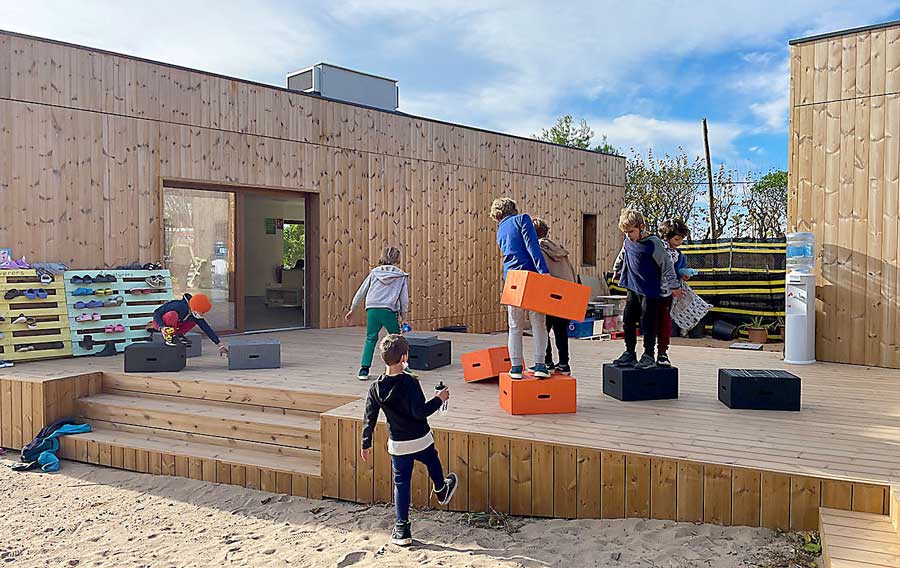

The versatility of Xbrick is demonstrated – where else – in practice. Here are some application examples that further illustrate the added value of the modules:
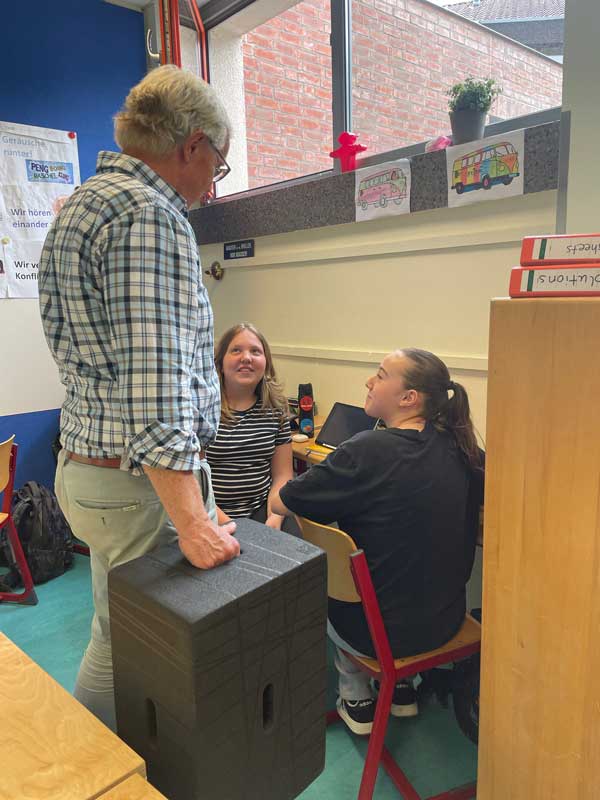
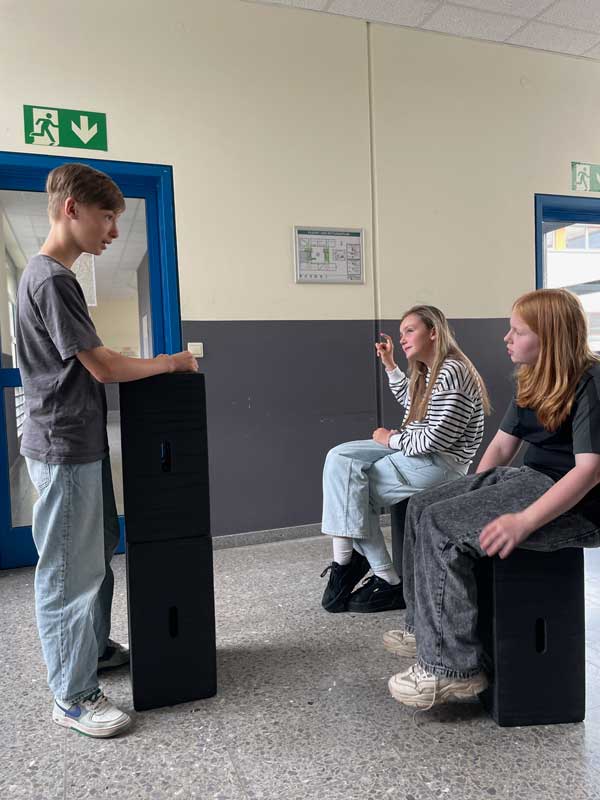
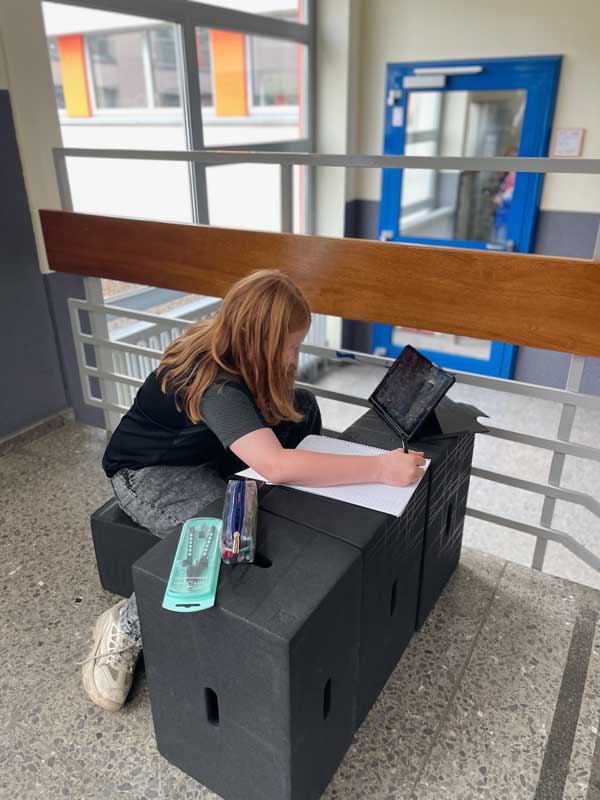



Learn more about how Xbrick is used in practice → Reference projects
The versatile Xbricks can be used to design creative games that combine learning and movement. Whether building, discussing or solving problems together – the Xbricks promote teamwork, motor skills and learning through play. Here are some examples of how you can make lessons more dynamic with Xbricks.
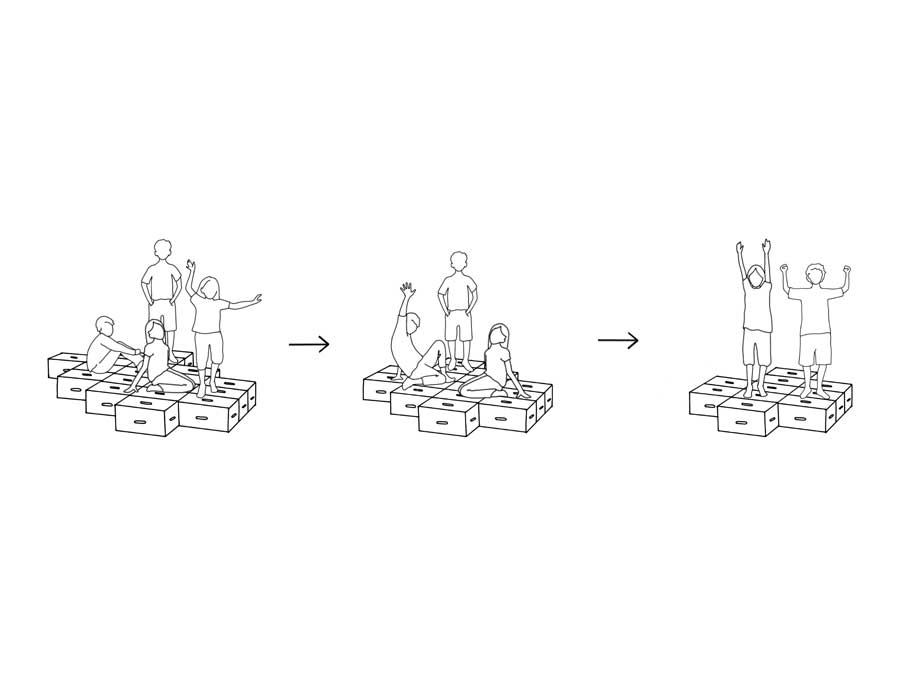
Participants and material: 2-4 teams, 5 students and 7 Xbricks per team.
Game setup: The Xbricks will laid out in a line, everyone stands on an designed. The person in front steps onto the new Xbrick and the team moves up. The team moves forward step by step without touching the ground.
Goal: The team that reaches the finish point first wins.
< strong>
Added value: “Ice floe” strengthens teamwork, coordination, balance and strategic thinking – and is a lot of fun!
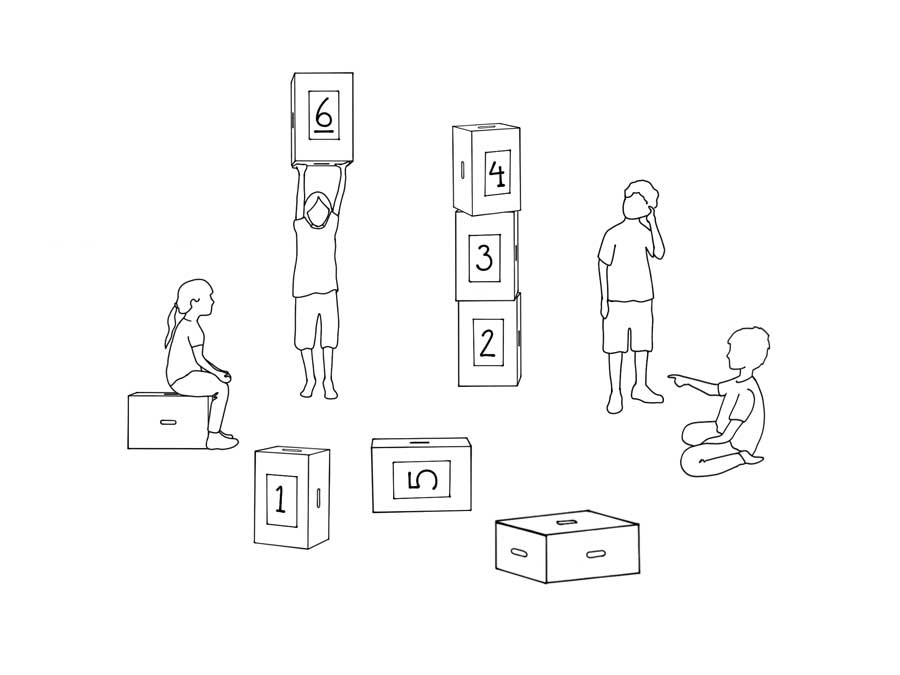
Participants and material: 2-4 children, 6 Xbricks with number cards (1-6).
Game setup: The Xbricks are placed in disorder placed on the floor.
Sequence of the game: The children work together to find the numbers in the correct order and stack the Xbricks accordingly. Tasks such as finding numbers, placing them and stacking them are distributed among the team.
Goal: All Xbricks must be stacked correctly from 1 to 6.
Added value:The game promotes numerical understanding, teamwork, communication and motor skills.
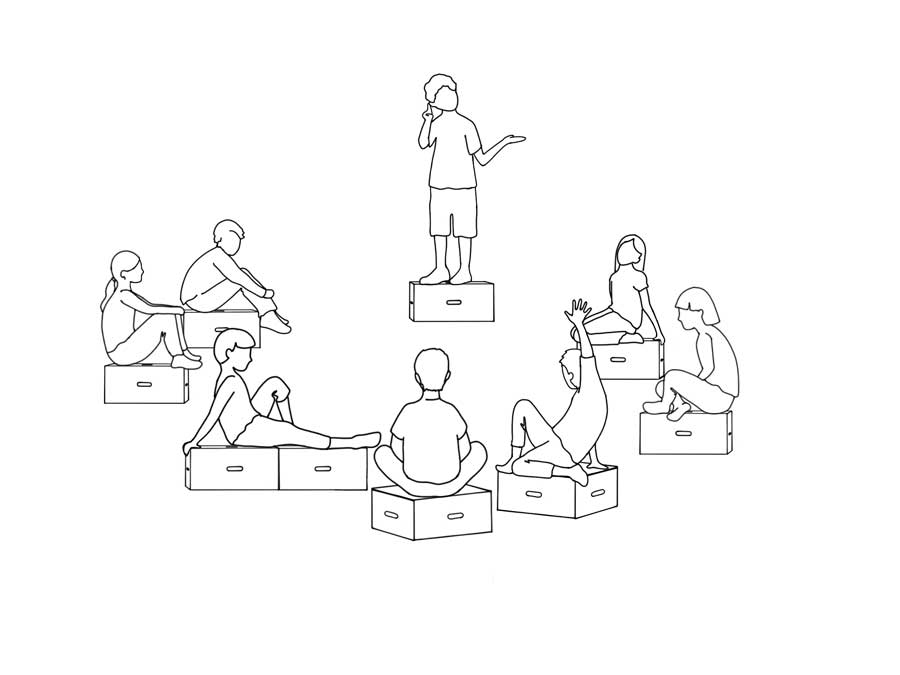
Participants and material: 6-10 children, 7-10 Xbricks (one per person, one for the speaker).
Game setup : The Xbricks are set up in a circle, one is in the middle or slightly offset for the speaker.
Gameplay: The children sit on them Xbricks in a circle while a child or the Teacher in the middle gives input (e.g. transfer of knowledge, task, discussion). The children can then take turns asking questions, expressing opinions or changing the role of presenter.
Aim: Open exchange and learning together in a structured environment.
< br />Added value: Promotes communication, listening, presentation skills and group dynamics. The Xbrick circle creates an active and collaborative learning atmosphere.
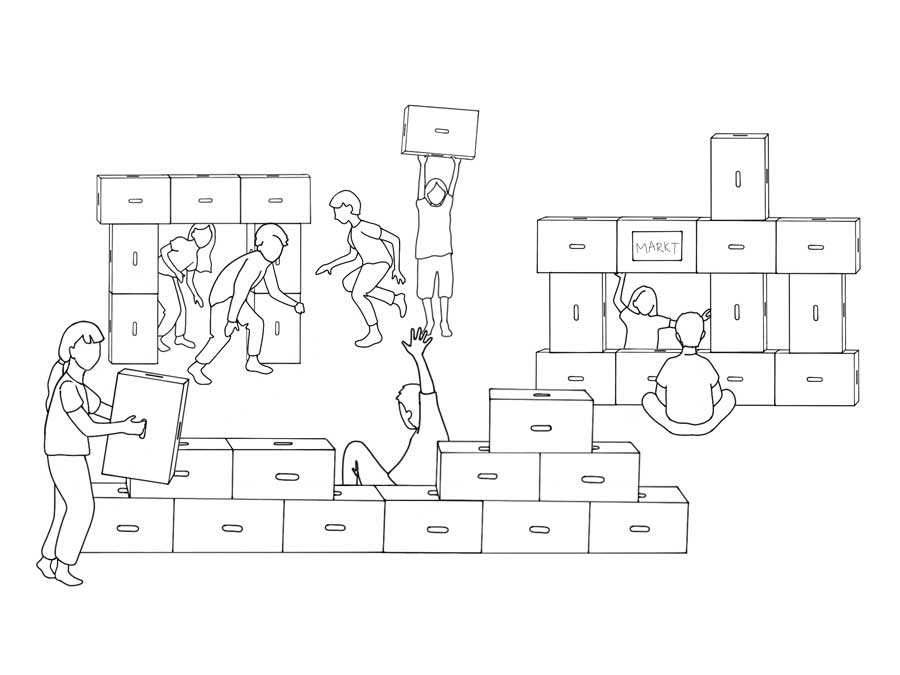
Participants and material: 4-8 children, at least 12 Xbricks, optionally with learning content (e.g. numbers, letters, symbols).
Game structure :The Xbricks are distributed around the room. Some may have educational content. Structures such as gates, walls or market stalls serve as targets and can visually underline different learning content.
Gameplay: The children build a structure together, e.g. B. a goal in which learning content on the Xbricks must be taken into account (e.g. numbers in the correct order or putting letters together to form a word). Other structures such as walls can visualize learning content such as sequences, patterns or concepts. After completion, they can use the building symbolically, such as walking through the gate or starting a new task. The tasks are distributed within the team.
Goal: Build different structures that integrate learning content and can be used creatively.
Added value: Promotes creativity, spatial thinking, teamwork and motor skills. Various buildings help to deepen learning content such as number or language understanding in a playful way.
Xbrick is more than a modular piece of furniture – it is a versatile tool that ideally supports modern learning concepts. With flexibility, mobility and sustainability, it offers a future-oriented solution for schools. Xbrick creates inspiring learning spaces that motivate students and teachers alike. The model relies on open learning landscapes in which students work autonomously and find creative solutions. Thanks to its easy adjustability, Xbrick fulfills a wide range of functions – from individual workstations to group tables to room dividers. It promotes self-organization and personal responsibility among learners, while making it easier to adapt spaces to changing needs.
Another highlight is the integration of exercise into everyday school life. Flexible sitting and standing options as well as the mobility of the modules increase concentration and physical activity, which has a positive effect on well-being and cognitive performance. At the same time, Xbrick is made of recyclable plastic, robust and durable – a sustainable, environmentally friendly investment in the educational infrastructure.
Whether as part of open learning landscapes, individual workstations, stage modules or sporting exercises – Xbrick offers countless possible uses. It combines flexibility, movement and sustainability, creating innovative learning spaces that meet the needs of modern schools. Xbrick stands for the change towards dynamic, inspiring learning environments that optimally prepare students for the future.
wd3 GmbH
Seidenstraße 57
70174 Stuttgart

Copyright © wd3 GmbH • 2025 • Xbrick® – Multifunctional furniture